Comparing Ethereum and Tron: An In-Depth Analysis of their Onchain Functionality – TronLink Wallet Trusted by over 10,000,000 users
Comparing Ethereum and Tron: An In-Depth Analysis of their Onchain Functionality
The world of blockchain technology is constantly evolving, with new platforms and networks emerging to offer innovative solutions to various industries. Two of the most prominent players in the blockchain space are Ethereum and Tron, each with their own unique features and capabilities.
Ethereum, often referred to as the “world computer,” is a decentralized platform that enables the creation and execution of smart contracts. It has gained widespread popularity for its ability to support a wide array of decentralized applications (dApps) and its robust development community. With its native cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH), Ethereum has become the go-to platform for developers and entrepreneurs looking to build decentralized solutions.
On the other hand, Tron is a blockchain-based platform that aims to decentralize the web by providing a platform for content creators to interact with their audiences directly. It boasts high transaction speeds and scalability, offering an ideal environment for the creation and distribution of digital content. Tron’s native cryptocurrency, TRX, fuels its ecosystem and enables users to participate in the network’s governance.
While Ethereum and Tron share the goal of decentralization, they differ in terms of their underlying technology and functionality. Ethereum relies on a proof-of-work consensus algorithm, whereas Tron utilizes a delegated proof-of-stake consensus mechanism. This difference in consensus algorithms affects the scalability, transaction speeds, and energy efficiency of each network. Furthermore, Ethereum has plans to transition to a proof-of-stake model, which could significantly enhance its scalability and energy efficiency.
In terms of functionality, both Ethereum and Tron support the creation and execution of smart contracts. However, Ethereum’s Solidity programming language enjoys wider adoption and support from the developer community. Tron, on the other hand, supports multiple programming languages, including Java and Solidity, offering developers more flexibility in choosing their preferred programming language.
As the blockchain industry continues to evolve, it is essential to understand the strengths and weaknesses of different platforms. Whether you are a developer, investor, or enthusiast, exploring the functionalities of Ethereum and Tron will provide you with insights into the capabilities and potential applications of these blockchain networks.
Understanding Ethereum and Tron Blockchains
The Ethereum and Tron blockchains are two of the most popular decentralized platforms for building and deploying smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). While they share some similarities, there are also key differences between the two that make them unique.
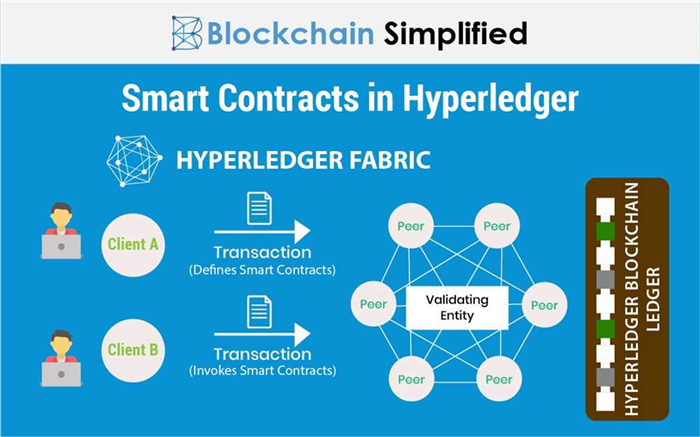
Ethereum was the first blockchain platform to introduce smart contracts, allowing developers to write and deploy code that executes automatically and without the need for intermediaries. It uses a virtual machine called the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) to execute these smart contracts. Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency is Ether (ETH), and it has its own consensus algorithm called Proof of Work (PoW).
Tron, on the other hand, was launched as a platform for the entertainment industry and aims to build a decentralized internet. It also supports smart contracts and DApps but has its own unique features. It uses the Tron Virtual Machine (TVM) to execute smart contracts, and its native cryptocurrency is Tronix (TRX). Tron utilizes a consensus algorithm called Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS), where a small number of elected nodes validate transactions and create new blocks.
One of the major differences between Ethereum and Tron is their scalability. Ethereum has been facing scalability issues due to its limited transaction processing capabilities, resulting in high fees and slow confirmation times. Tron, on the other hand, claims to have faster transaction speeds and lower fees, making it more scalable for DApps with high transaction volumes.
Another difference is the development community and ecosystem. Ethereum has a larger and more established development community, with a wide range of tools, libraries, and frameworks available for developers to build on. It has a strong presence in the decentralized finance (DeFi) space and has enabled the creation of various financial applications. Tron, on the other hand, has been focusing on the entertainment industry and has attracted developers working on gaming and content delivery applications.
Both Ethereum and Tron have their strengths and weaknesses, and the choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the project. Ethereum offers a more established ecosystem and a wide range of supported applications, while Tron provides faster transaction speeds and lower fees. Understanding the differences and similarities between these blockchains is crucial when choosing the right platform for building decentralized applications.
Key Differences in Onchain Functionality
When comparing the onchain functionality of Ethereum and Tron, several key differences emerge. These differences can greatly impact the user experience, consensus mechanism, and scalability of each blockchain.
Ethereum, being the first smart contract platform, has a more mature and robust onchain functionality compared to Tron. It offers a wide variety of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contract capabilities. Ethereum’s Solidity programming language allows developers to create complex and highly customizable smart contracts, making it a preferred choice for building decentralized applications.
On the other hand, Tron focuses on providing high throughput and scalability. It uses delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) as its consensus mechanism, allowing for faster block confirmations and a higher transaction throughput. This makes Tron suitable for applications that require fast and frequent transactions, such as online gaming and content distribution.
Another key difference is the approach to governance. Ethereum has a decentralized governance model where decisions are made by the community through onchain voting and discussions. Tron, however, has a more centralized governance model where decisions are made by its foundation and founder, Justin Sun. This centralized approach has its advantages in terms of efficiency and quick decision-making, but it also raises concerns about censorship and censorship resistance.
Furthermore, Ethereum has a more active and vibrant developer community, with a larger number of developers contributing to the ecosystem. This leads to a wider range of tools, libraries, and resources available to Ethereum developers. Tron is still relatively new and has a smaller developer community, which may limit the availability of resources and support for developers.
In summary, Ethereum and Tron have different strengths and weaknesses in terms of onchain functionality. Ethereum offers a more mature and robust smart contract platform, while Tron focuses on high throughput and scalability. The governance models of each blockchain also differ, with Ethereum’s decentralized approach contrasting with Tron’s more centralized decision-making process. Consider these factors when choosing a blockchain platform for your specific use case.
Use Cases and Future Perspectives

Both Ethereum and Tron have a wide range of use cases and have shown great potential for future growth and development.
Ethereum
Ethereum has established itself as the leading smart contract platform, and has been widely adopted by developers and businesses alike. Some of the key use cases of Ethereum include:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Ethereum has become the go-to platform for the development of decentralized financial applications, such as lending platforms, decentralized exchanges, and stablecoins.
- NFTs: Ethereum’s support for non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has sparked a new wave of innovation in the digital art, gaming, and collectibles industries.
- Supply Chain Management: Ethereum’s transparency and immutability make it a suitable platform for managing supply chains and ensuring the authenticity of products.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Ethereum enables the creation of DAOs, which are organizations governed by smart contracts and operate without the need for centralized authority.
Looking into the future, Ethereum has an ambitious roadmap that includes several upgrades, such as Ethereum 2.0. This upgrade aims to improve scalability, security, and sustainability, making Ethereum even more suitable for mass adoption.
Tron
Tron, on the other hand, has positioned itself as a blockchain platform for decentralized applications (DApps) and entertainment services. Some notable use cases of Tron include:
- Entertainment Content Sharing: Tron aims to disrupt the traditional entertainment industry by enabling content creators to directly share and monetize their work without intermediaries.
- Gaming: Tron has gained popularity among game developers due to its high throughput and low transaction fees, making it a preferred platform for building blockchain-based games.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEX): Tron has a growing ecosystem of decentralized exchanges, enabling users to trade tokens directly from their wallets without the need for a centralized exchange.
- Tokenization and Crowdfunding: Tron enables the tokenization of assets and the creation of crowdfunding campaigns, making it easier for individuals and businesses to raise funds.
In the future, Tron aims to further expand its ecosystem and attract more developers and users through its initiatives, such as Project Atlas and the BitTorrent integration. Tron also plans to improve its consensus algorithm to enhance scalability and performance.
In conclusion, both Ethereum and Tron offer a wide range of use cases and have promising future perspectives. While Ethereum dominates the smart contract space, Tron focuses on entertainment and DApps. Both platforms are continuously evolving and pushing the boundaries of blockchain technology.
What is the main difference between Ethereum and Tron blockchains?
The main difference between Ethereum and Tron blockchains lies in their consensus mechanisms. Ethereum uses a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus algorithm, while Tron employs a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) algorithm.
How are smart contracts executed on the Ethereum and Tron blockchains?
Smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain are executed using the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which is a Turing-complete runtime environment. On the Tron blockchain, smart contracts are executed using the Tron Virtual Machine (TVM).
Can Ethereum and Tron blockchains handle the same level of transaction throughput?
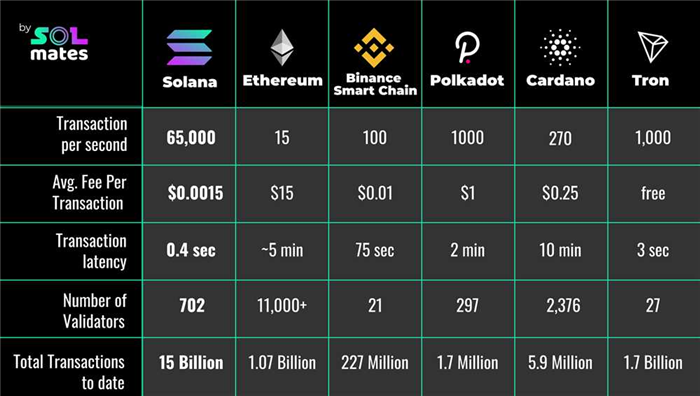
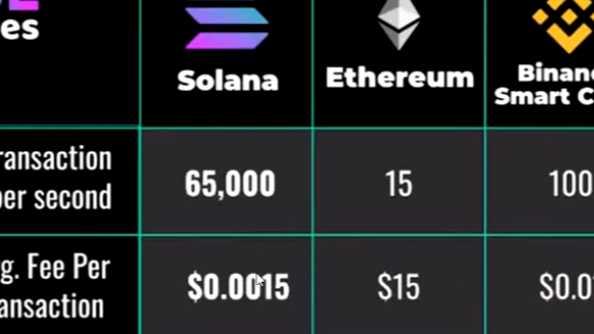
No, Ethereum and Tron blockchains have different levels of transaction throughput. Currently, Ethereum can handle around 15 transactions per second, while Tron claims to be able to handle up to 2,000 transactions per second.
How do Ethereum and Tron blockchains handle scalability?
Ethereum is working on implementing various scalability solutions, such as the upcoming Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, which will introduce the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm. Tron, on the other hand, claims to have achieved high scalability through its DPoS consensus algorithm and use of sidechains.